How are Blood Samples Transported Safely?
Release time: 2025-04-21
When transporting blood samples, strict specifications need to be followed to ensure the integrity and accuracy of the samples and to prevent contamination or degradation. The transport requirements for different types of blood samples will also be different, such as serum, plasma, whole blood, etc.
Post-collection processing
Separation of serum or plasma: After blood is collected, if the sample needs to be separated into serum or plasma, centrifugation should be performed as soon as possible. Serum or plasma needs to be separated within an appropriate time to avoid the influence of cells on sample components.
Blood collection tube selection: Choose appropriate blood collection tubes according to the test items, such as tubes containing anticoagulants (such as EDTA tubes, heparin tubes) or tubes without anticoagulants.
Transport temperature requirements
Room temperature transport:
Whole blood and blood routine samples can be transported at room temperature, but should be sent to the laboratory as soon as possible to reduce transportation time and avoid long-term exposure of blood samples to inappropriate temperatures.
Refrigerated transport:
Serum and plasma samples need to be refrigerated and kept at a temperature between 2°C and 8°C. Ice packs and refrigerators are used to keep the temperature low to prevent sample deterioration.
Frozen transport:
Samples for long-term storage, such as genomic analysis/biomarkers, need to be frozen for transportation, and the temperature should be kept at -20°C or lower. Cell or virus samples may require ultra-low temperature transportation with liquid nitrogen (-196°C).
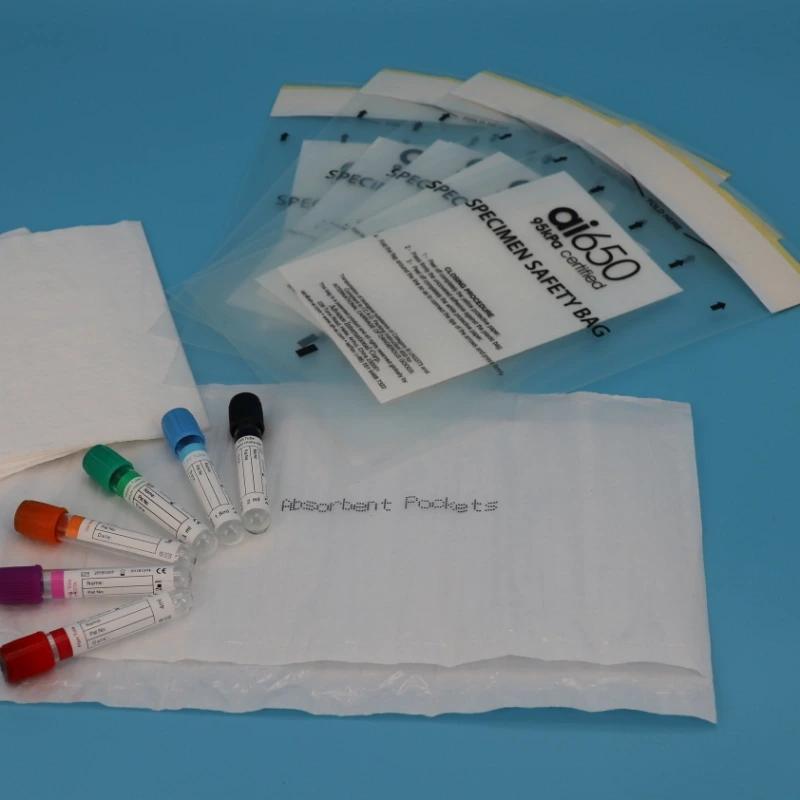
Containers and packaging
Shockproof packaging: To prevent the sample from being shaken during transportation, the blood sample should be packaged with shockproof materials (such as foam, bubble film).
Sealed containers: Use containers with good sealing performance to prevent leakage or contamination, such as vacuum blood collection tubes.
Clear labeling: Each sample must be clearly labeled with patient information, sampling time and sample type to avoid confusion.
Transportation time and speed
Shorten transportation time: The transportation time should be controlled within the shortest time to avoid the blood sample being affected by the long transportation time, and it should be delivered to the laboratory within 2 hours.
Choose a professional transportation company: When the sample needs to be transported across cities or over a long distance, choose a professional medical sample transportation company to ensure the safety and compliance of the sample.
Special precautions
Avoid high temperature exposure: High temperature will accelerate the degradation of blood samples. Avoid direct sunlight or exposure to high temperature during transportation.
Clarify transportation requirements: Before transportation, you should understand the laboratory’s temperature and storage requirements for samples in detail to ensure that they meet their requirements.
Comply with laws and regulations: Blood sample transportation packaging should comply with relevant laws and regulations, especially the safe transportation requirements for infectious diseases and biological samples.
Transportation documents
Transportation documents: Ensure that the transportation documents are complete, including sample instructions, transportation requirements and recipient information, to ensure smooth processing by the laboratory.
By following these specifications, you can ensure that the blood sample remains intact during transportation, avoid sample contamination and degradation, and ensure the accuracy of subsequent test results.