What are absorbent pads for specimen transport?
Release time: 2025-03-13
When transporting biological or chemical specimens, maintaining their integrity and preventing contamination is critical. One unsung hero in this process is the absorbent pad—a simple yet vital component of specimen transport systems. Whether you work in healthcare, research, or diagnostics, understanding the role of absorbent pads can enhance safety, compliance, and reliability. Let’s explore why these pads matter and how to choose the right ones.
What Are Absorbent Pads?
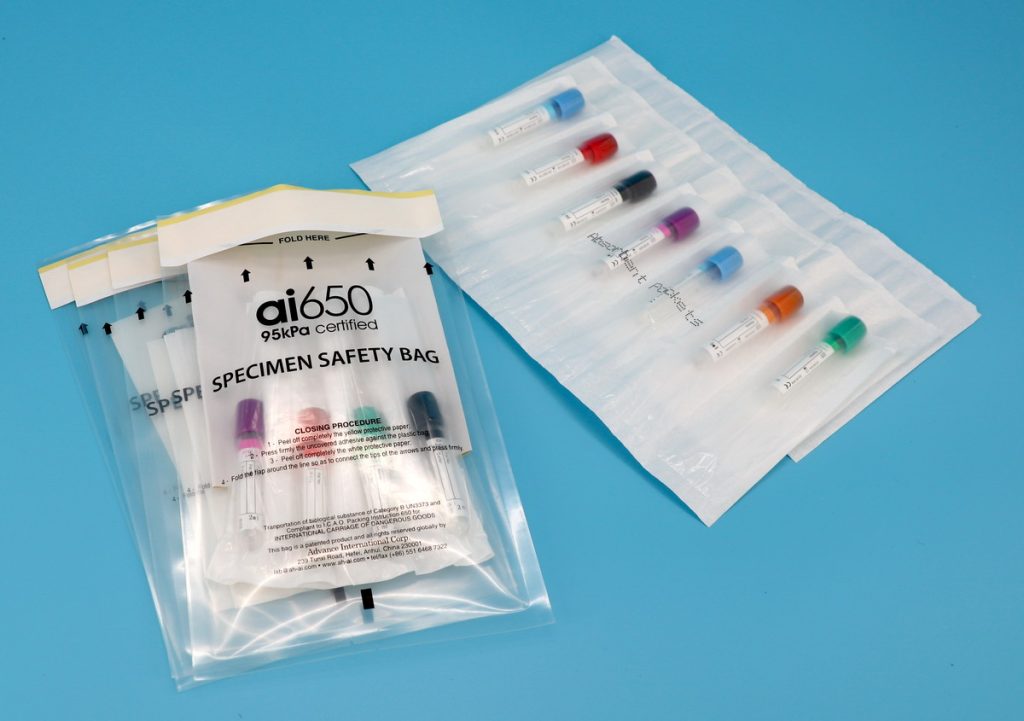
Absorbent pads are specialized materials designed to soak up liquids, control moisture, and prevent leaks during the transport of specimens. They are commonly placed inside containers, coolers, or packaging alongside sample tubes, vials, or culture plates. Made from materials like cellulose, superabsorbent polymers (SAP), or layered composites, these pads act as a safeguard against spills that could compromise samples or pose biohazard risks.
Why Are They Essential for Specimen Transport?
- Leak Prevention:
- Accidental spills of blood, urine, chemicals, or microbial cultures can damage samples, contaminate other items, or endanger handlers. Absorbent pads trap liquids quickly, minimizing cross-contamination.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Many industries, including healthcare and biotech, must adhere to strict guidelines (e.g., IATA, WHO, or CDC) for safe specimen transport. Absorbent pads help meet requirements for secondary containment and spill control.
- Sample Preservation: Excess moisture can degrade sensitive samples. Pads wick away liquid, maintaining optimal humidity levels and preventing bacterial growth or chemical reactions.
- Safety: By neutralizing spills, these pads reduce exposure to hazardous substances, protecting lab personnel, couriers, and recipients.
Types of Absorbent Pads
Not all absorbent pads are created equal. Key variations include:
- Universal Absorbent Pads:
Ideal for general use with water-based liquids (e.g., blood, saline). Often made of cellulose or recycled materials. - Chemical-Resistant Pads:
Treated to handle aggressive solvents, acids, or alkalis without degrading. - Biohazard-Specific Pads:
Designed with antimicrobial coatings to neutralize pathogens in spills. - Reusable vs. Disposable:
Eco-friendly reusable pads (e.g., washable cellulose) suit low-risk scenarios, while disposable options are preferred for biohazards.
How to Choose the Right Absorbent Pad
- Assess the Specimen Type:
- Match the pad’s absorbency and material compatibility to your samples (e.g., viral cultures vs. chemical reagents).
- Consider Volume:
- Ensure the pad’s capacity exceeds the maximum liquid volume in your containers.
Check Regulatory Requirements:
Verify if pads need certifications (e.g., UN-approved packaging for hazardous materials).
Prioritize Sustainability:
Opt for biodegradable or reusable pads if environmental impact is a concern.
- Best Practices for Using Absorbent Pads
- Layer Smartly: Place pads beneath and around specimens inside transport containers.
- Seal Securely: Use leak-proof containers even with pads as an added precaution.
- Dispose Responsibly: Follow biohazard waste protocols for contaminated pads.
- Train Staff: Ensure teams understand proper pad placement and spill response.