Which Specimen is the Most Frequently Utilized?
Release time: 2025-02-26
In the realm of medical diagnostics and research, the collection, transport, and analysis of specimens are critical processes that ensure accurate results and effective patient care. Among the various types of specimens collected, blood is arguably the most frequently utilized. Blood samples provide a wealth of information, from basic metabolic panels to complex genetic analyses, making them indispensable in modern medicine. However, the journey of a blood specimen from collection to analysis involves several crucial steps, including the use of specialized equipment such as specimen transport bags and specimen tubes.
The Importance of Blood Specimens
Blood is a versatile specimen that can be used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, including infections, metabolic disorders, and chronic diseases. It is also essential for monitoring treatment efficacy and patient health over time. The frequency with which blood specimens are utilized is a testament to their diagnostic value. In hospitals, clinics, and laboratories worldwide, blood samples are collected daily, often in large volumes, to meet the demands of patient care and medical research.
The Role of Specimen Tubes
The collection of blood specimens typically involves the use of specimen tubes, which are designed to preserve the integrity of the sample until it can be analyzed. These tubes come in various types, each containing specific additives that serve different purposes. For example, EDTA tubes are used for hematology tests, while heparin tubes are preferred for chemistry analyses. The choice of tube depends on the type of test being conducted, and proper selection is crucial to ensure accurate results.
Specimen tubes are often color-coded to indicate their contents and intended use, reducing the risk of errors during collection and processing. Once the blood is drawn into the tube, it is essential to mix the sample gently with the additive to prevent clotting or hemolysis, which could compromise the quality of the specimen.
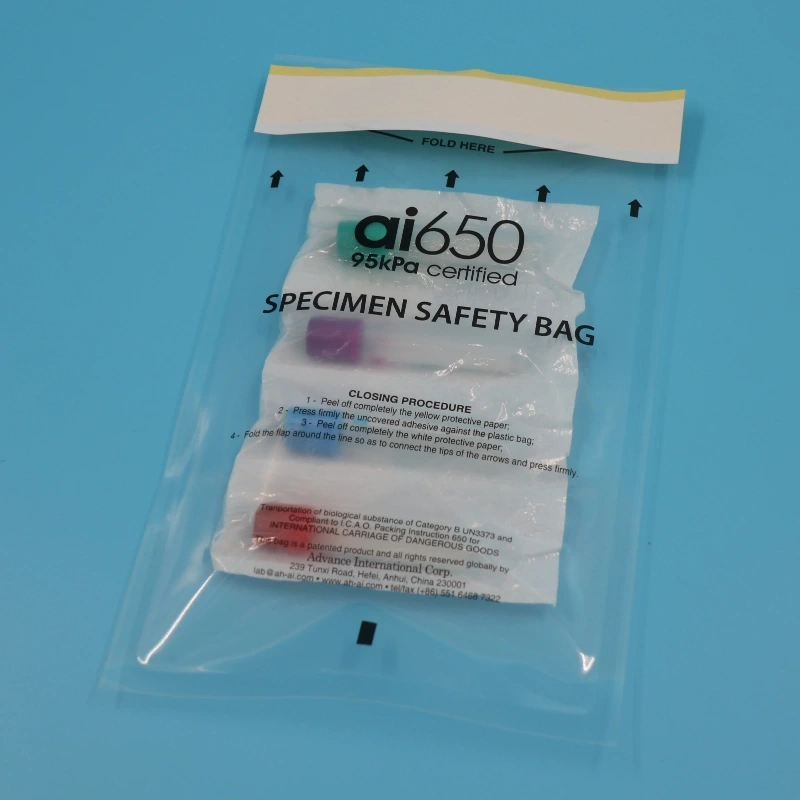
The Role of Specimen Transport Bags
After collection, blood specimens must be transported to the laboratory for analysis. This is where specimen transport bags come into play. These bags are designed to protect the specimen from external contaminants, temperature fluctuations, and physical damage during transit. They often feature insulation to maintain the sample at the required temperature, especially for tests that are sensitive to thermal changes.
Specimen transport bags also play a critical role in ensuring the safety of laboratory personnel. Many of these bags are equipped with biohazard labels and leak-proof seals to prevent exposure to potentially infectious materials. In addition, they are often designed to accommodate multiple specimen tubes, allowing for the efficient transport of several samples at once.

Challenges in Specimen Transport
Despite the advancements in specimen transport technology, challenges remain. One of the most significant issues is the risk of sample degradation during transit. Prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures or improper handling can lead to inaccurate test results, potentially affecting patient care. To mitigate these risks, healthcare facilities must adhere to strict protocols for specimen collection, labeling, and transport.
Another challenge is the need for timely delivery. In many cases, blood specimens must be analyzed within a specific timeframe to ensure the accuracy of the results. Delays in transport can lead to delays in diagnosis and treatment, underscoring the importance of efficient logistics and reliable transport systems.
Blood specimens are undoubtedly the most frequently utilized in medical diagnostics, owing to their versatility and the wealth of information they provide. The use of specimen tubes and specimen transport bags is integral to the process, ensuring that samples are collected, preserved, and transported safely and efficiently. As medical science continues to advance, the importance of these tools will only grow, highlighting the need for ongoing innovation and adherence to best practices in specimen handling.